Headline News
What is anarcho-capitalism?

Both viewpoints of anarcho-capitalism and libertarianism share the goal of limited government, according to Classical Liberal Organization faculty advisor and Chairman of Economics Charles Steele.
In a Feb. 18 event hosted by the Classical Liberal Organization and alumnus Christian Betz ’20, students discussed the viability of anarcho-capitalism and the similar ideology of libertarianism.
Steele, who joked that he alternates between anarcho-capitalism and libertarianism depending on the day of the week, opened the event with brief remarks on the topic of “What is Anarcho-capitalism?”
“I believe the government should be as small as possible,” Steele said. “It’s a good saying to get that across.”
He defined anarcho-capitalism as a system in which the private sector provides all goods and services on a for-profit basis, including public goods typically associated with government, such as law enforcement services.
After Steele’s remarks, Betz, who joined via Zoom, summarized similarities and differences between anarcho-capitalism and libertarianism. He presented each ideology’s view of the role of government, the efficacy of the free market to provide goods and services, social contract theory, and the non-aggression principle (the idea that the use of force on a person or his property is inherently unjust.)
While Betz noted that he grew up with sympathies for the “ancap,” shorthand for anarcho-capitalist, he credited his Hillsdale education for shifting his beliefs toward minarchism, a school of libertarian thought which argues that the scope of government should be limited to providing a few essential public goods like law enforcement, a military, and courts.
“I can’t say any particular professor, but my education overall at Hillsdale pushed me in a direction toward minarchism coming from a more ancap set of ideals before that,” Betz said. “Just my time at Hillsdale, growing up, learning more, etc., my views shifted more gradually.”
After Betz spoke, the event was opened up to discussion among the roughly 25 audience members. Nearly everyone in attendance contributed to the discussion.
Junior Luke Sherman spoke in favor of anarcho-capitalism, criticizing libertarians for holding an inconsistent view of social contract theory.
“Anarcho-capitalism is the logical conclusion of libertarianism. There’s a lot of problems with social contract theory, mainly the idea that if you don’t like it you can leave, which denies private property rights,” Sherman said. “If you start from the premise that the government derives its authority from the consent of the governed, you ultimately have to say that individuals can choose to not consent to government without leaving. You have to have explicit consent from each individual member of society in order to claim that the government derives its power from consent.”
Senior and Classical Liberal Organization President Haakon Santaella praised the quality of discussion and enthusiasm of participants.
“There were a lot of energetic participants to discuss the presentation between each side,” Santaella said. “It was a good, open, intellectually honest discussion. Both sides presented fair points.”
In addition to focusing on which ideology is morally correct, Santaella said he would have liked for the discussion to address which position would be more practical.
“Implicit in the libertarian argument was that this is something that works and is desirable as opposed to anarcho-capitalism,” he said. “There is a question about whether the outcomes of anarcho-capitalism are desirable and whether they are desirable in contrast to the outcomes of social contract theory in the U.S. Constitution.”
Steele agreed.
“Another thing is whether an ancap system can exist or function,” he said. “I think the answer is yes, but certain conditions must be met for it to be a stable system and function the way we hope it would. On the other hand, these may be the same conditions for a limited state like we supposedly have under the Constitution. It’s a two-edged sword.”
Despite the differences between libertarianism and anarcho-capitalism, most participants seemed to agree on the importance of coming together to tackle a shared enemy: the tyranny of unlimited government.
“The person a libertarian hates the most is a libertarian who believes slightly differently than them,” Betz said. “We agree on a lot of things and want a lot of the same ideals. We can all support each other and push towards that ideal.”
Sherman agreed.
“My position is that I think if we’re going to have a system of government, I think you should be involved in the process, and I don’t think it’s self-contradictory to the anarchist position,” he said. “At the end of the day, libertarians and anarchists have much more in common than we do differences.”

Headline News
How Canadian churches are helping their communities cope with the wildfires

As wildfires burn across Canada, churches are finding ways to support their members and the broader community directly impacted by the crisis.
According to the Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre, as of June 13, there are 462 active fires across Canada – and 236 of them classified as out of control fires.
Whether it’s through phone calls or donations to community members, here’s how a few churches across Canada are handling active wildfires and the aftermath in their regions.
Westwood Hills, N.S.: St. Nicholas Anglican Church
In Nova Scotia, St. Nicholas Anglican Church and other churches in the area are collecting money for grocery cards to give to families impacted by the Tantallon wildfire.
Right outside of Halifax, N.S., the Tantallon wildfire destroyed 151 homes. More than 16,000 people evacuated the area due to the fire.
The fire is now considered contained, but Tanya Moxley, the treasurer at St. Nicholas is organizing efforts to get grocery gift cards into the hands of impacted families.
As of June 12, four churches in the area – St. Nicholas, Parish of French Village, St Margaret of Scotland and St John the Evangelist – raised nearly $3,500. The money will be split for families’ groceries between five schools in the area impacted by the wildfire.
Moxley said she felt driven to raise this money after she heard the principal of her child’s school was using his own money to buy groceries for impacted families in their area.
“[For] most of those people who were evacuated, the power was off in their subdivision for three, four or five days,” she said. “Even though they went home and their house was still standing, the power was off and they lost all their groceries.”
Moxley said many people in the area are still “reeling” from the fires. She said the church has an important role to help community members during this time.
“We’re called to feed the hungry and clothe the naked and house the homeless and all that stuff, right? So this is it. This is like where the rubber hits the road.”
Headline News
Is it ever OK to steal from a grocery store?

Mythologized in the legend of Robin Hood and lyricized in Les Misérables, it’s a debate as old as time: is it ever permissible to steal food? And if so, under what conditions? Now, amid Canada’s affordability crisis, the dilemma has extended beyond theatrical debate and into grocery stores.
Although the idea that theft is wrong is both a legally enshrined and socially accepted norm, the price of groceries can also feel criminally high to some — industry data shows that grocery stores can lose between $2,000 and $5,000 a week on average from theft. According to Statistics Canada, most grocery item price increases surged by double digits between 2021 and 2022. To no one’s surprise, grocery store theft is reportedly on the rise as a result. And if recent coverage of the issue rings true, some Canadians don’t feel bad about shoplifting. But should they?
Kieran Oberman, an associate professor of philosophy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in the United Kingdom, coined the term “re-distributive theft” in his 2012 paper “Is Theft Wrong?” In simplest terms, redistributive theft is based on the idea that people with too little could ethically take from those who have too much.
“Everybody, when they think about it, accepts that theft is sometimes permissible if you make the case extreme enough,” Oberman tells me over Zoom. “The question is, when exactly is it permissible?”
Almost no one, Oberman argues, believes the current distribution of wealth across the world is just. We have an inkling that theft is bad, but that inequality is too. As more and more Canadians feel the pinch of inflation, grocery store heirs accumulate riches — Loblaw chair and president Galen Weston, for instance, received a 55 percent boost in compensation in 2022, taking in around $8.4 million for the year. Should someone struggling with rising prices feel guilty when they, say, “forget” to scan a bundle of zucchini?
Headline News
The homeless refugee crisis in Toronto illustrates Canada’s broken promises
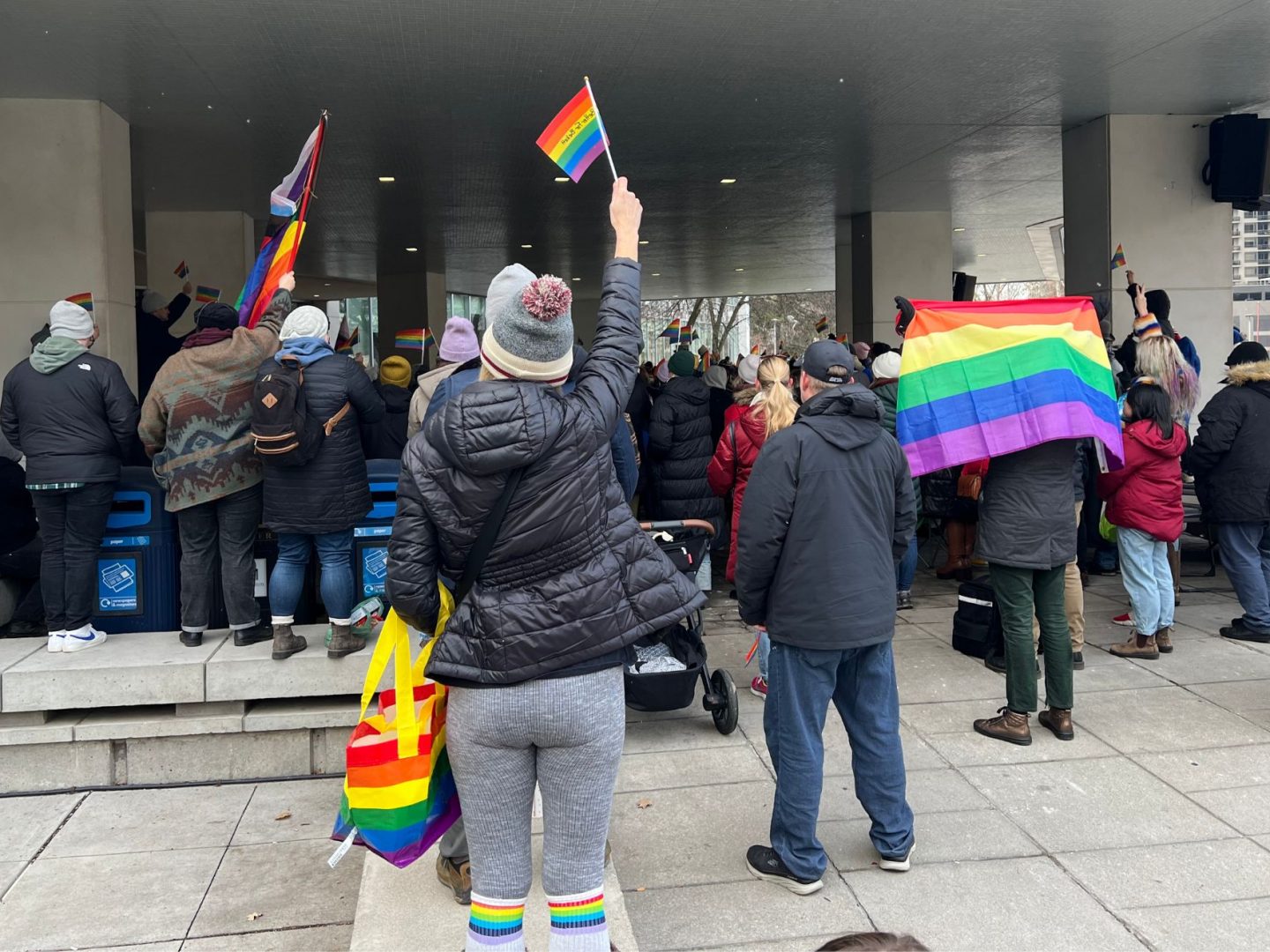
UPDATE 07/18/2023: A coalition of groups arranged a bus to relocate refugees to temporarily stay at a North York church on Monday evening, according to CBC, CP24 and Toronto Star reports.
Canadians live in a time of threadbare morality. Nowhere is this more obvious than in Toronto’s entertainment district, where partygoers delight in spending disposable income while skirting refugees sleeping on sidewalks. The growing pile of luggage at the downtown corner of Peter and Richmond streets resembles the lost baggage section at Pearson airport but is the broken-hearted terminus at the centre of a cruel city.
At the crux of a refugee funding war between the municipal and federal governments are those who have fled persecution for the promise of Canada’s protection. Until June 1, asylum seekers used to arrive at the airport and be sent to Toronto’s Streets to Homes Referral Assessment Centre at 129 Peter St. in search of shelter beds. Now, Toronto’s overcrowded shelter system is closed to these newcomers, so they sleep on the street.
New mayor Olivia Chow pushed the federal government Wednesday for at least $160 million to cope with the surge of refugees in the shelter system. She rightly highlights that refugees are a federal responsibility. In response, the department of Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada points to hundreds of millions in dollars already allocated to cities across Canada through the Interim Housing Assistance Program, while Ontario says it has given nearly $100 million to organizations that support refugees. But these efforts are simply not enough to deliver on Canada’s benevolent promise to the world’s most vulnerable.
The lack of federal generosity and finger-pointing by the city has orchestrated a moral crisis. It’s reminiscent of the crisis south of the border, where Texas governor Greg Abbott keeps bussing migrants to cities located in northern Democratic states. Without the necessary resources, information, and sometimes the language skills needed to navigate the bureaucratic mazes, those who fled turbulent homelands for Canada have become political pawns.
But Torontonians haven’t always been this callous.
In Ireland Park, at Lake Ontario’s edge, five statues of gaunt and grateful refugees gaze at their new home: Toronto circa 1847. These statues honour a time when Toronto, with a population of only 20,000 people, welcomed 38,500 famine-stricken migrants from Ireland. It paralleled the “Come From Away” event of 9/11 in Gander, N.L., where the population doubled overnight, and the people discovered there was indeed more than enough for all. It was a time when the city lived up to its moniker as “Toronto, The Good.”
Now, as a wealthy city of three million people, the city’s residents are tasked with supporting far fewer newcomers. Can we not recognize the absurdity in claiming scarcity?