Headline News
Peacebuilder Clubs create momentum for peace within communities

We launched our Peacebuilder Clubs program at the Rotary International Convention in Toronto. Peacebuilder Clubs were pioneered eight years ago by past Rotarian Action Group for Peace (RAGFP) Board Member and Past District 5100 Governor Mike Caruso as a way of building support for the six Rotary Peace Centers around the world. With the support of RAGFP, District 5100 registered 21 Peacebuilder Clubs in Oregon and Washington, USA. Last year our RAGFP leadership team was determined to champion this program in Rotary clubs worldwide as an essential call to action for Rotarian peacebuilders.
Peacebuilder Clubs allow Rotarians to gather regularly and focus on peace, discuss peace action, and educate their community about Rotarian principles of peacebuilding. Peacebuilder Clubs establish peace projects and initiatives within Rotary clubs and districts that often involve bringing together local community members who may never have opportunities to meet otherwise. Since we first introduced the program at the Toronto 2018 Convention, Peacebuilder Clubs have formed in Africa, Asia, Australia, Canada, Europe, the Middle East, Serbia and throughout the United States. Rotarians understand how fellowship through Rotary is a force for good and positive change in our world.

Below are some examples of what Peacebuilders Clubs are doing:
- The Rotary Club of Bornheim in Germany became a Peacebuilder Club in September 2018. The club is involved in many projects and initiatives that fill important gaps and build bridges of hope for immigrants and displaced youth caused by the refugee crisis in Europe. According to Reuters, since 2014 more than 1.6 million people seeking asylum have entered Germany. The club is working on a global grant project that aims to integrate refugees, especially children who arrive in Germany unaccompanied, into communities and the greater society by promoting peaceful political dialogue between strangers, neighbors, and immigrants. The club is also working on educating youth and promoting participation in the democratic process.
- The Rotary Club of Three Creeks in Vancouver, Washington, USA is a Peacebuilder Club active in Rotary Peacebuilder District 5100. As public political discourse took a turn for the worse in the United States, their Peacebuilder Committee Co-Chair Dan Sockle began wondering how Rotarians can share Rotary’s guiding principles of friendship and service with non-Rotarians of all political backgrounds and opinions.
Better Angels is a program that Dan, RAGFP members, and other Rotarian peacebuilders are using to inspire peaceful and healthy political discourse. Better Angels offers events and education designed to “depolarize America.” Their Red/Blue Workshops visit cities across America and feature activities, listening exercises, and co-operative skills training designed to get people talking and listening to one another.

RAGFP Founder Al Jubitz plants a Peace Pole with Peacebuilder Club, the Rotary Club of Kona Sunrise, Hawaii USA

RAGFP Executive Director and Rotary Peace Fellow Reem Ghunaim along with McMinnville Rotary Assistant Governor Larry Strober.
Establishing Peacebuilder Clubs is a major part of our mission at RAGFP. As part of the world’s greatest humanitarian organizations, we are all peacebuilders. Please join us on this path. Download the step-by-step Peacebuilder Club instructions to recruit and establish a new Peacebuilder Club. (Locate all RAGFP Peacebuilder Clubs on our Peacebuilder Clubs Map.)
Join or donate to Rotarian Action Group for Peace to help engage, empower and educate Rotarian peacebuilders around the world. For details, contact the Rotarian Action Group for Peace at contact@rotariansforpeace.org.
Headline News
How Canadian churches are helping their communities cope with the wildfires

As wildfires burn across Canada, churches are finding ways to support their members and the broader community directly impacted by the crisis.
According to the Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre, as of June 13, there are 462 active fires across Canada – and 236 of them classified as out of control fires.
Whether it’s through phone calls or donations to community members, here’s how a few churches across Canada are handling active wildfires and the aftermath in their regions.
Westwood Hills, N.S.: St. Nicholas Anglican Church
In Nova Scotia, St. Nicholas Anglican Church and other churches in the area are collecting money for grocery cards to give to families impacted by the Tantallon wildfire.
Right outside of Halifax, N.S., the Tantallon wildfire destroyed 151 homes. More than 16,000 people evacuated the area due to the fire.
The fire is now considered contained, but Tanya Moxley, the treasurer at St. Nicholas is organizing efforts to get grocery gift cards into the hands of impacted families.
As of June 12, four churches in the area – St. Nicholas, Parish of French Village, St Margaret of Scotland and St John the Evangelist – raised nearly $3,500. The money will be split for families’ groceries between five schools in the area impacted by the wildfire.
Moxley said she felt driven to raise this money after she heard the principal of her child’s school was using his own money to buy groceries for impacted families in their area.
“[For] most of those people who were evacuated, the power was off in their subdivision for three, four or five days,” she said. “Even though they went home and their house was still standing, the power was off and they lost all their groceries.”
Moxley said many people in the area are still “reeling” from the fires. She said the church has an important role to help community members during this time.
“We’re called to feed the hungry and clothe the naked and house the homeless and all that stuff, right? So this is it. This is like where the rubber hits the road.”
Headline News
Is it ever OK to steal from a grocery store?
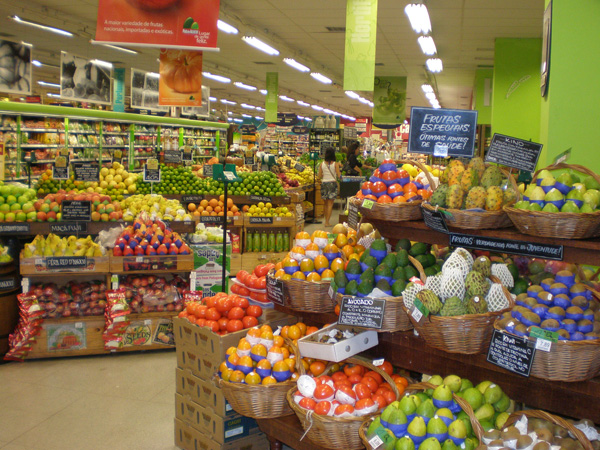

Mythologized in the legend of Robin Hood and lyricized in Les Misérables, it’s a debate as old as time: is it ever permissible to steal food? And if so, under what conditions? Now, amid Canada’s affordability crisis, the dilemma has extended beyond theatrical debate and into grocery stores.
Although the idea that theft is wrong is both a legally enshrined and socially accepted norm, the price of groceries can also feel criminally high to some — industry data shows that grocery stores can lose between $2,000 and $5,000 a week on average from theft. According to Statistics Canada, most grocery item price increases surged by double digits between 2021 and 2022. To no one’s surprise, grocery store theft is reportedly on the rise as a result. And if recent coverage of the issue rings true, some Canadians don’t feel bad about shoplifting. But should they?
Kieran Oberman, an associate professor of philosophy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in the United Kingdom, coined the term “re-distributive theft” in his 2012 paper “Is Theft Wrong?” In simplest terms, redistributive theft is based on the idea that people with too little could ethically take from those who have too much.
“Everybody, when they think about it, accepts that theft is sometimes permissible if you make the case extreme enough,” Oberman tells me over Zoom. “The question is, when exactly is it permissible?”
Almost no one, Oberman argues, believes the current distribution of wealth across the world is just. We have an inkling that theft is bad, but that inequality is too. As more and more Canadians feel the pinch of inflation, grocery store heirs accumulate riches — Loblaw chair and president Galen Weston, for instance, received a 55 percent boost in compensation in 2022, taking in around $8.4 million for the year. Should someone struggling with rising prices feel guilty when they, say, “forget” to scan a bundle of zucchini?
Headline News
The homeless refugee crisis in Toronto illustrates Canada’s broken promises
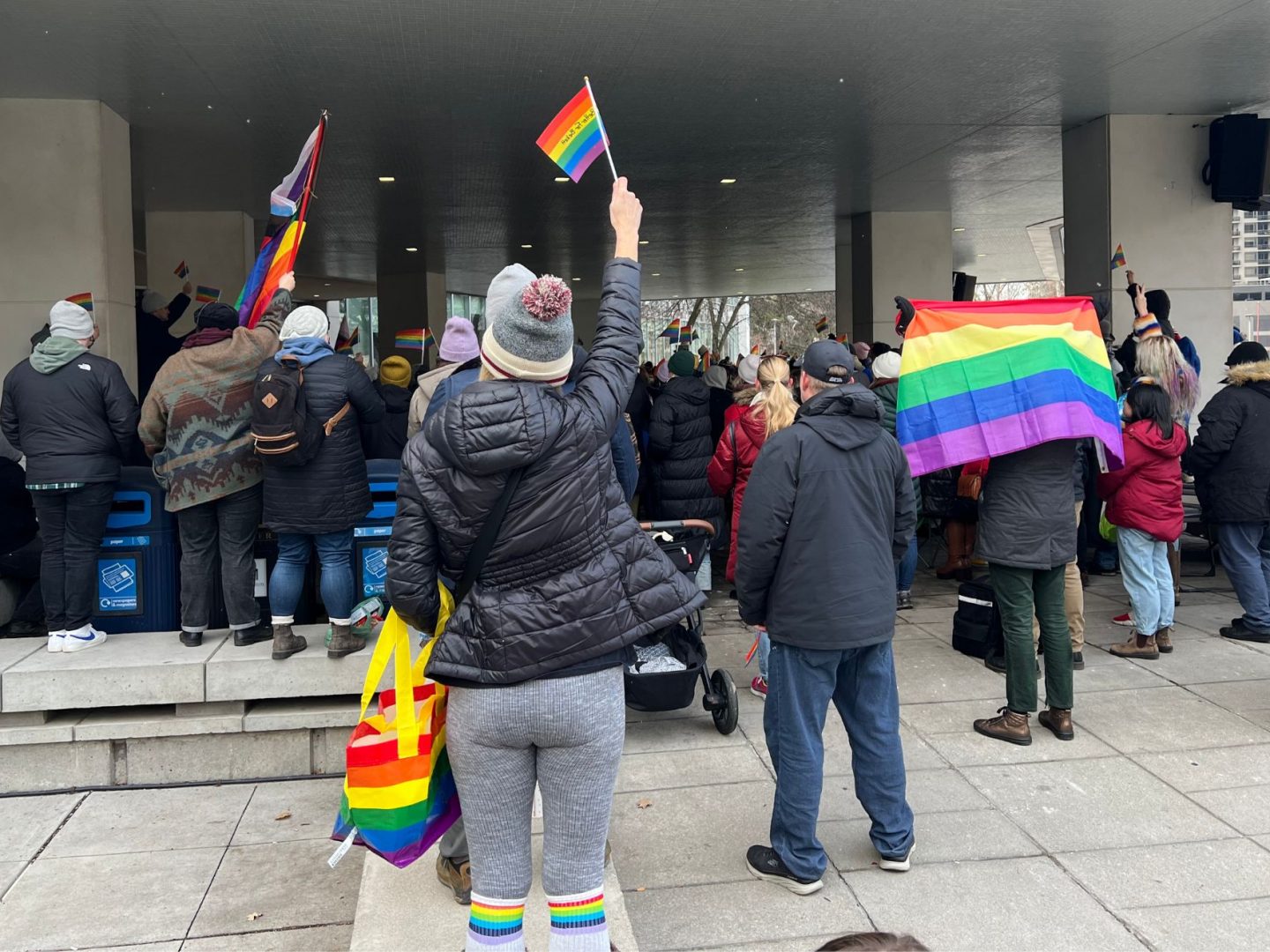
UPDATE 07/18/2023: A coalition of groups arranged a bus to relocate refugees to temporarily stay at a North York church on Monday evening, according to CBC, CP24 and Toronto Star reports.
Canadians live in a time of threadbare morality. Nowhere is this more obvious than in Toronto’s entertainment district, where partygoers delight in spending disposable income while skirting refugees sleeping on sidewalks. The growing pile of luggage at the downtown corner of Peter and Richmond streets resembles the lost baggage section at Pearson airport but is the broken-hearted terminus at the centre of a cruel city.
At the crux of a refugee funding war between the municipal and federal governments are those who have fled persecution for the promise of Canada’s protection. Until June 1, asylum seekers used to arrive at the airport and be sent to Toronto’s Streets to Homes Referral Assessment Centre at 129 Peter St. in search of shelter beds. Now, Toronto’s overcrowded shelter system is closed to these newcomers, so they sleep on the street.
New mayor Olivia Chow pushed the federal government Wednesday for at least $160 million to cope with the surge of refugees in the shelter system. She rightly highlights that refugees are a federal responsibility. In response, the department of Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada points to hundreds of millions in dollars already allocated to cities across Canada through the Interim Housing Assistance Program, while Ontario says it has given nearly $100 million to organizations that support refugees. But these efforts are simply not enough to deliver on Canada’s benevolent promise to the world’s most vulnerable.
The lack of federal generosity and finger-pointing by the city has orchestrated a moral crisis. It’s reminiscent of the crisis south of the border, where Texas governor Greg Abbott keeps bussing migrants to cities located in northern Democratic states. Without the necessary resources, information, and sometimes the language skills needed to navigate the bureaucratic mazes, those who fled turbulent homelands for Canada have become political pawns.
But Torontonians haven’t always been this callous.
In Ireland Park, at Lake Ontario’s edge, five statues of gaunt and grateful refugees gaze at their new home: Toronto circa 1847. These statues honour a time when Toronto, with a population of only 20,000 people, welcomed 38,500 famine-stricken migrants from Ireland. It paralleled the “Come From Away” event of 9/11 in Gander, N.L., where the population doubled overnight, and the people discovered there was indeed more than enough for all. It was a time when the city lived up to its moniker as “Toronto, The Good.”
Now, as a wealthy city of three million people, the city’s residents are tasked with supporting far fewer newcomers. Can we not recognize the absurdity in claiming scarcity?
-

 Lifestyle8 months ago
Lifestyle8 months agoOntario Line subway construction permanently shuts down beloved Toronto bakery
-

 Business8 months ago
Business8 months agoThe Canadian Armed Forces are hiring for several non-combat military jobs
-

 Business8 months ago
Business8 months agoPorter’s new loyalty program promises to match Air Canada’s Aeroplan status
-

 Business8 months ago
Business8 months agoPeople call out Sobeys for ridiculous prices after another expensive find at Ontario store
-

 Business8 months ago
Business8 months ago‘Here, everything feels much closer’: Entrepreneur says leaving Toronto for Innisfil good for business
-

 Lifestyle8 months ago
Lifestyle8 months agoCanada considers capping international student visas to address housing crisis
-

 Lifestyle8 months ago
Lifestyle8 months agoWoman crashes car and runs around highway with bottle of booze on typical day in Toronto
-

 Business8 months ago
Business8 months agoBeauty Week is back at Hudson’s Bay in Toronto and it’s time to get glam



