Headline News
Empowering women in Colombian prisons
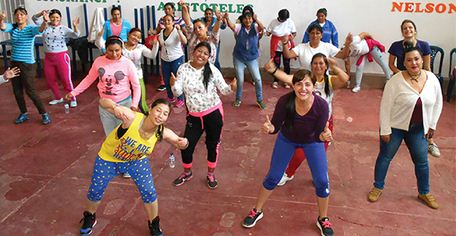
I had to go to prison to understand how education for innovation is the path for empowering millions of Latin American and Caribbean women economically. I’ve never committed a crime; I belong to that group of people who believe education is the most sophisticated tool we have to opening any door.
In 2016, I founded MujeresConDerechos.org with the idea of reminding society that all girls and all women are powerful. For this reason, I have dedicated myself to gathering the most influential leaders through summits, marches, and a television program. The attention and support I have received has been converted into generating innovative programs for girls and women most in need.
We had an amazing opportunity in October 2017 to put into practice the methodology of innovation I had created at Harvard University and that I had successfully tested with 1,500 youths living in rural areas of Mexico and Colombia. Now, I would be able to test my theories with 170 women in a medium-security prison in Sogamoso, within Boyacá.
The first day we visited them, the other women who went with me left terrified. A prison is a hell designed to disempower and mutilate human potential daily. However, I insisted we return and begin our program, “Nuevos Comienzos Innovando” (Innovative New Beginnings). The first two months, we dedicated ourselves to working with them on the concepts of confidence, forgiveness, strength, peace, and leadership.
It was incredible to see over a short period of time how these ladies went from being hermits and melancholy, to participating and hopeful with our process. By 22 December 2017, we were capable of laughing, crying, and hugging while we planned powerful goals for a better future.

Charlie Ruth Castro leads an exercise class for inmates.
A prison is a hell designed to disempower and mutilate human potential daily.
My methodology for digital empowerment bases itself on a very simple principle: we are all capable of seeing ourselves as superheroes through the use of innovation when we put our strength to resolving the more general and common problems affecting our community.
These ladies have come to understand that the three problems most affecting women in prison are their separation from their children, the lack of information regarding staying healthy in a highly unhealthy space, and interpersonal disputes about debts owed, that end in shocking punishments, such as the infamous “dungeon” – a dark, cold, and repugnant space where they could be held for up to 72 hours.
With these women, I’ve had the most profound discussions about justice, the economy of crime, liberty, and transcendence. The methodology we used has inspired them to plan their own brand and line of beauty products made from organic herbs. Those least interested in these persons having a decent job and re-entering society are the public servants of the National Penitentiary and Prison Institute of Columbia. The challenges, as well as humiliation, they have produced for the team and the women of our program are innumerable. But advocating for a more just society demands arming yourself with patience, and being creative in order to focus on the solutions and not the problems.
The majority of the women who took part in my program arrived at this prison due to crimes such as drug microtrafficking and theft; some landed here for homicide, kidnapping, or extortion. Almost all of them are mothers, and nearly a third of them are the second generation in their families to commit a crime. Most come from rural areas and bands of poverty within medium-sized cities. Almost all of them chased the fantasy of making money and becoming self-sufficient via the activities that led them to crime. A great many of them know their legal past will mark them and if they do not learn appropriate work skills or work on themselves from within, they are condemned to repeat the same mistake on the outside.
However there are two things that almost all these women share: they come from an impoverished Colombia and they face a culture that is violent against girls and women. My team and I feel grateful these women allowed us to research and work on a reality that affects so many. Despite how difficult it is to believe, we have concluded prisons are where we will find the potential to transform the country. Yes – impossible to believe, but they are.
The women in this prison made it possible for me to understand that the inequality and violence we see in the world today has its origins in gender inequality and lack of access to an empowering education for millions of girls and women.
It is time to invest in the education of innovation for our girls and young women. If we equip them with the tools that allow them to understand problems as opportunities for solution, or go as far as to teach them to use new technologies to create sources of employment, and to achieve excellence in the jobs of today and tomorrow, we can secure their economic empowerment, and we will be supporting the innovative and sustainable industrialization of our countries.
Charlie Ruth was one of six young innovators recognized during Rotary Day at the United Nations in Nairobi, Kenya, in November. Read more about the innovators. Follow Charlie Ruth Castro @CharlieRuth
Headline News
How Canadian churches are helping their communities cope with the wildfires

As wildfires burn across Canada, churches are finding ways to support their members and the broader community directly impacted by the crisis.
According to the Canadian Interagency Forest Fire Centre, as of June 13, there are 462 active fires across Canada – and 236 of them classified as out of control fires.
Whether it’s through phone calls or donations to community members, here’s how a few churches across Canada are handling active wildfires and the aftermath in their regions.
Westwood Hills, N.S.: St. Nicholas Anglican Church
In Nova Scotia, St. Nicholas Anglican Church and other churches in the area are collecting money for grocery cards to give to families impacted by the Tantallon wildfire.
Right outside of Halifax, N.S., the Tantallon wildfire destroyed 151 homes. More than 16,000 people evacuated the area due to the fire.
The fire is now considered contained, but Tanya Moxley, the treasurer at St. Nicholas is organizing efforts to get grocery gift cards into the hands of impacted families.
As of June 12, four churches in the area – St. Nicholas, Parish of French Village, St Margaret of Scotland and St John the Evangelist – raised nearly $3,500. The money will be split for families’ groceries between five schools in the area impacted by the wildfire.
Moxley said she felt driven to raise this money after she heard the principal of her child’s school was using his own money to buy groceries for impacted families in their area.
“[For] most of those people who were evacuated, the power was off in their subdivision for three, four or five days,” she said. “Even though they went home and their house was still standing, the power was off and they lost all their groceries.”
Moxley said many people in the area are still “reeling” from the fires. She said the church has an important role to help community members during this time.
“We’re called to feed the hungry and clothe the naked and house the homeless and all that stuff, right? So this is it. This is like where the rubber hits the road.”
Headline News
Is it ever OK to steal from a grocery store?
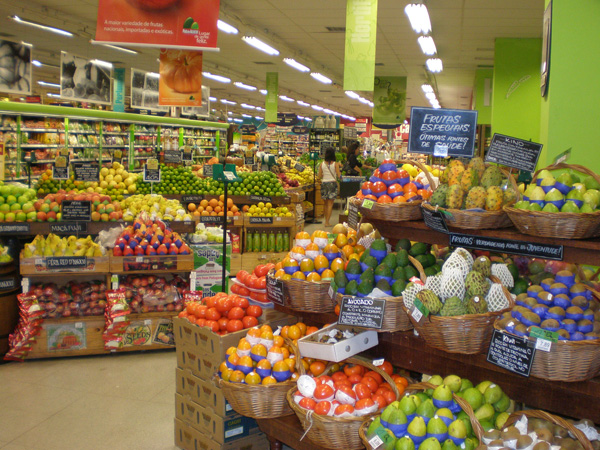

Mythologized in the legend of Robin Hood and lyricized in Les Misérables, it’s a debate as old as time: is it ever permissible to steal food? And if so, under what conditions? Now, amid Canada’s affordability crisis, the dilemma has extended beyond theatrical debate and into grocery stores.
Although the idea that theft is wrong is both a legally enshrined and socially accepted norm, the price of groceries can also feel criminally high to some — industry data shows that grocery stores can lose between $2,000 and $5,000 a week on average from theft. According to Statistics Canada, most grocery item price increases surged by double digits between 2021 and 2022. To no one’s surprise, grocery store theft is reportedly on the rise as a result. And if recent coverage of the issue rings true, some Canadians don’t feel bad about shoplifting. But should they?
Kieran Oberman, an associate professor of philosophy at the London School of Economics and Political Science in the United Kingdom, coined the term “re-distributive theft” in his 2012 paper “Is Theft Wrong?” In simplest terms, redistributive theft is based on the idea that people with too little could ethically take from those who have too much.
“Everybody, when they think about it, accepts that theft is sometimes permissible if you make the case extreme enough,” Oberman tells me over Zoom. “The question is, when exactly is it permissible?”
Almost no one, Oberman argues, believes the current distribution of wealth across the world is just. We have an inkling that theft is bad, but that inequality is too. As more and more Canadians feel the pinch of inflation, grocery store heirs accumulate riches — Loblaw chair and president Galen Weston, for instance, received a 55 percent boost in compensation in 2022, taking in around $8.4 million for the year. Should someone struggling with rising prices feel guilty when they, say, “forget” to scan a bundle of zucchini?
Headline News
The homeless refugee crisis in Toronto illustrates Canada’s broken promises
UPDATE 07/18/2023: A coalition of groups arranged a bus to relocate refugees to temporarily stay at a North York church on Monday evening, according to CBC, CP24 and Toronto Star reports.
Canadians live in a time of threadbare morality. Nowhere is this more obvious than in Toronto’s entertainment district, where partygoers delight in spending disposable income while skirting refugees sleeping on sidewalks. The growing pile of luggage at the downtown corner of Peter and Richmond streets resembles the lost baggage section at Pearson airport but is the broken-hearted terminus at the centre of a cruel city.
At the crux of a refugee funding war between the municipal and federal governments are those who have fled persecution for the promise of Canada’s protection. Until June 1, asylum seekers used to arrive at the airport and be sent to Toronto’s Streets to Homes Referral Assessment Centre at 129 Peter St. in search of shelter beds. Now, Toronto’s overcrowded shelter system is closed to these newcomers, so they sleep on the street.
New mayor Olivia Chow pushed the federal government Wednesday for at least $160 million to cope with the surge of refugees in the shelter system. She rightly highlights that refugees are a federal responsibility. In response, the department of Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada points to hundreds of millions in dollars already allocated to cities across Canada through the Interim Housing Assistance Program, while Ontario says it has given nearly $100 million to organizations that support refugees. But these efforts are simply not enough to deliver on Canada’s benevolent promise to the world’s most vulnerable.
The lack of federal generosity and finger-pointing by the city has orchestrated a moral crisis. It’s reminiscent of the crisis south of the border, where Texas governor Greg Abbott keeps bussing migrants to cities located in northern Democratic states. Without the necessary resources, information, and sometimes the language skills needed to navigate the bureaucratic mazes, those who fled turbulent homelands for Canada have become political pawns.
But Torontonians haven’t always been this callous.
In Ireland Park, at Lake Ontario’s edge, five statues of gaunt and grateful refugees gaze at their new home: Toronto circa 1847. These statues honour a time when Toronto, with a population of only 20,000 people, welcomed 38,500 famine-stricken migrants from Ireland. It paralleled the “Come From Away” event of 9/11 in Gander, N.L., where the population doubled overnight, and the people discovered there was indeed more than enough for all. It was a time when the city lived up to its moniker as “Toronto, The Good.”
Now, as a wealthy city of three million people, the city’s residents are tasked with supporting far fewer newcomers. Can we not recognize the absurdity in claiming scarcity?